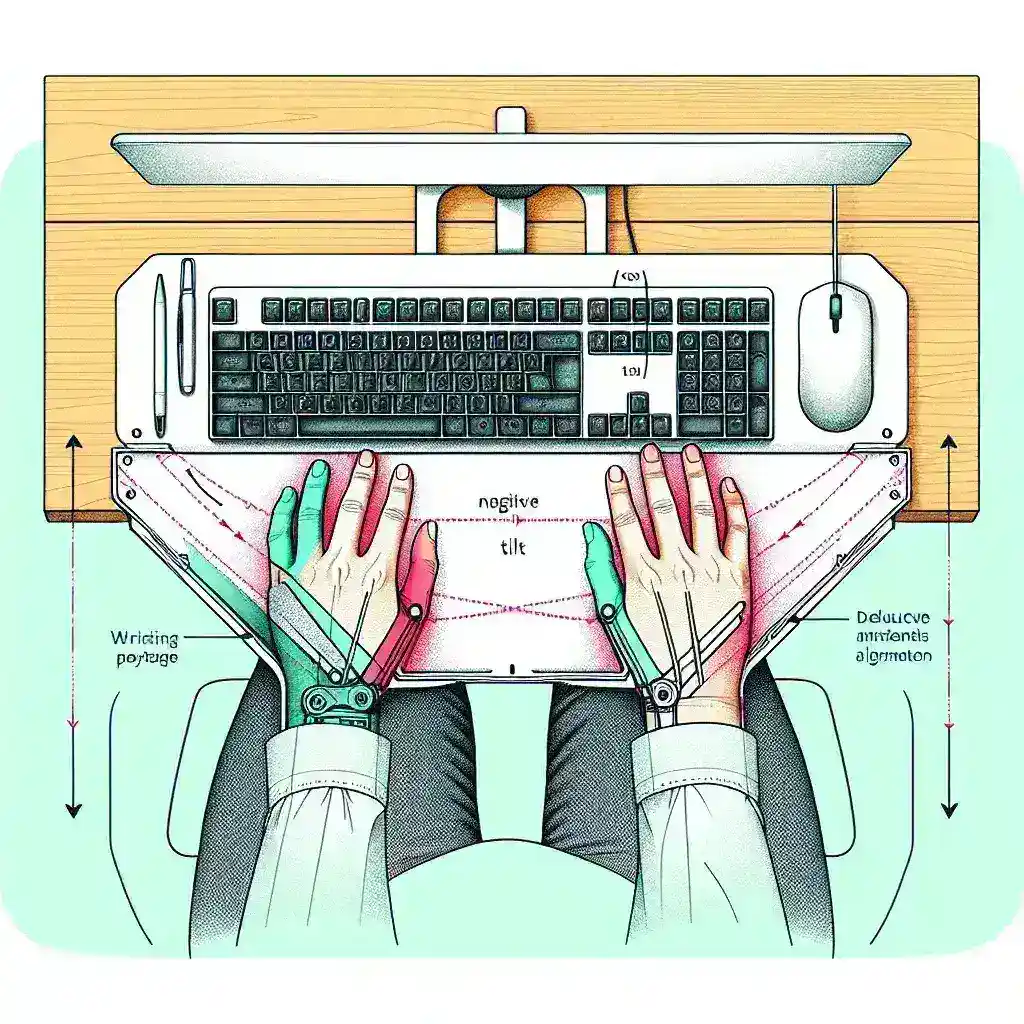
In the modern office environment, long hours at a desk can lead to various musculoskeletal problems, particularly wrist strain. One of the innovative solutions to this problem is the ergonomic keyboard tray with negative tilt. This specialized equipment is designed to promote a more natural wrist and hand position while working. But how exactly does it help reduce wrist strain? Let’s explore the science and benefits behind this ergonomic solution.
What is a Negative Tilt Keyboard Tray?
An ergonomic keyboard tray with negative tilt slopes downward, positioning the keyboard at a decline relative to the front of the workstation. This design enables users to type with their wrists in a more neutral, less strained position. Here is a basic comparison between traditional keyboard trays and those with negative tilt.
| Feature | Traditional Keyboard Tray | Negative Tilt Keyboard Tray |
|---|---|---|
| Wrist Position | Extends upward | Neutral or downward |
| Typing Angle | Flat or upward slant | Negative slant |
| Risk of Strain | High | Reduced |
How Negative Tilt Reduces Wrist Strain
Neutral Wrist Position
One of the primary reasons ergonomic keyboard trays with a negative tilt are beneficial is because they promote a neutral wrist position. When your wrists are straight or slightly downward, there’s less tension on the carpal tunnel, reducing the risk of conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Reduction in Flexion and Extension
Traditional keyboard setups often force the wrists into prolonged flexion (bent upward) or extension (bent downward). Both positions can increase strain on wrist muscles and tendons. A negative tilt helps keep the wrists in a more natural, relaxed position.
The Benefits of Using an Ergonomic Keyboard Tray
Improved Posture
Using a keyboard tray with a negative tilt can help improve overall posture. When the wrists are positioned more naturally, it encourages a better arm and shoulder posture, reducing the risk of upper body strain.
Enhanced Comfort
Comfort is significantly enhanced when using a negatively-tilted keyboard tray. The natural wrist position reduces discomfort and fatigue, making it easier to work for extended periods.
Boosted Productivity
With reduced strain and increased comfort, productivity can see a considerable boost. Workers are less likely to take breaks due to discomfort, leading to more consistent and efficient work.
Choosing the Right Ergonomic Keyboard Tray
When it comes to selecting the best ergonomic keyboard tray, there are several factors to consider:
- Adjustability: Opt for a tray that offers multiple adjustments for height and tilt.
- Quality Materials: Ensure the tray is made of durable materials to withstand daily use.
- Ease of Installation: Choose a tray that’s easy to install and integrates well with your existing setup.
- Additional Features: Some trays come with a mouse platform or wrist pads for added comfort.
Conclusion
Ergonomic keyboard trays with a negative tilt can significantly reduce wrist strain by promoting natural hand positioning, reducing flexion and extension, and improving overall posture. By considering factors like adjustability and quality, you can find the perfect tray to meet your needs and enhance your comfort and productivity at work.